Table of Contents
A bladeless wind turbine is a cylindrical device designed to convert wind energy into electricity by vibrating at a resonance frequency. This innovative technology utilizes the resonance between airflow and the structure's natural frequency (aeroelastic resonance) to power an alternator system.
Bladeless wind energy is an alternative to solar panels and traditional wind turbines. The notable advantages of bladeless turbines are reduced maintenance cost, prolonged life, environmental benefits, and operation in urban areas with less wind.
According to Blackridge’s Global Power Market Forecast Report, Global electricity demand is expected to rise faster over the next three years, growing by an average of 3.4% annually through 2026. Bladeless wind power generators are one step closer to the future, replacing traditional blade wind turbines characterized by large rotating blades, noise pollution, bird strikes, and visual impact.
Bladeless wind power generation will be more advanced in 2025 with more patenting trends in bladeless wind turbine technology. This notable increase reflects the heightened interest and investment in this sector in the near future. Let’s explore bladeless wind turbine technology in detail.
What Are Bladeless Wind Turbines, and How Do They Work?

Bladeless wind turbines generate electricity from the wind without using traditional wind turbine models. Instead, they use a phenomenon called vortex shedding, where swirling patterns of air (vortices) are created when wind flows past a cylindrical structure.
These turbines are designed to harness the energy from these vortices, causing the cylinder to vibrate. This vibration, known as Vortex Induced Vibration (VIV), is converted into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electricity using an alternator.
Bladeless Wind Turbine Design
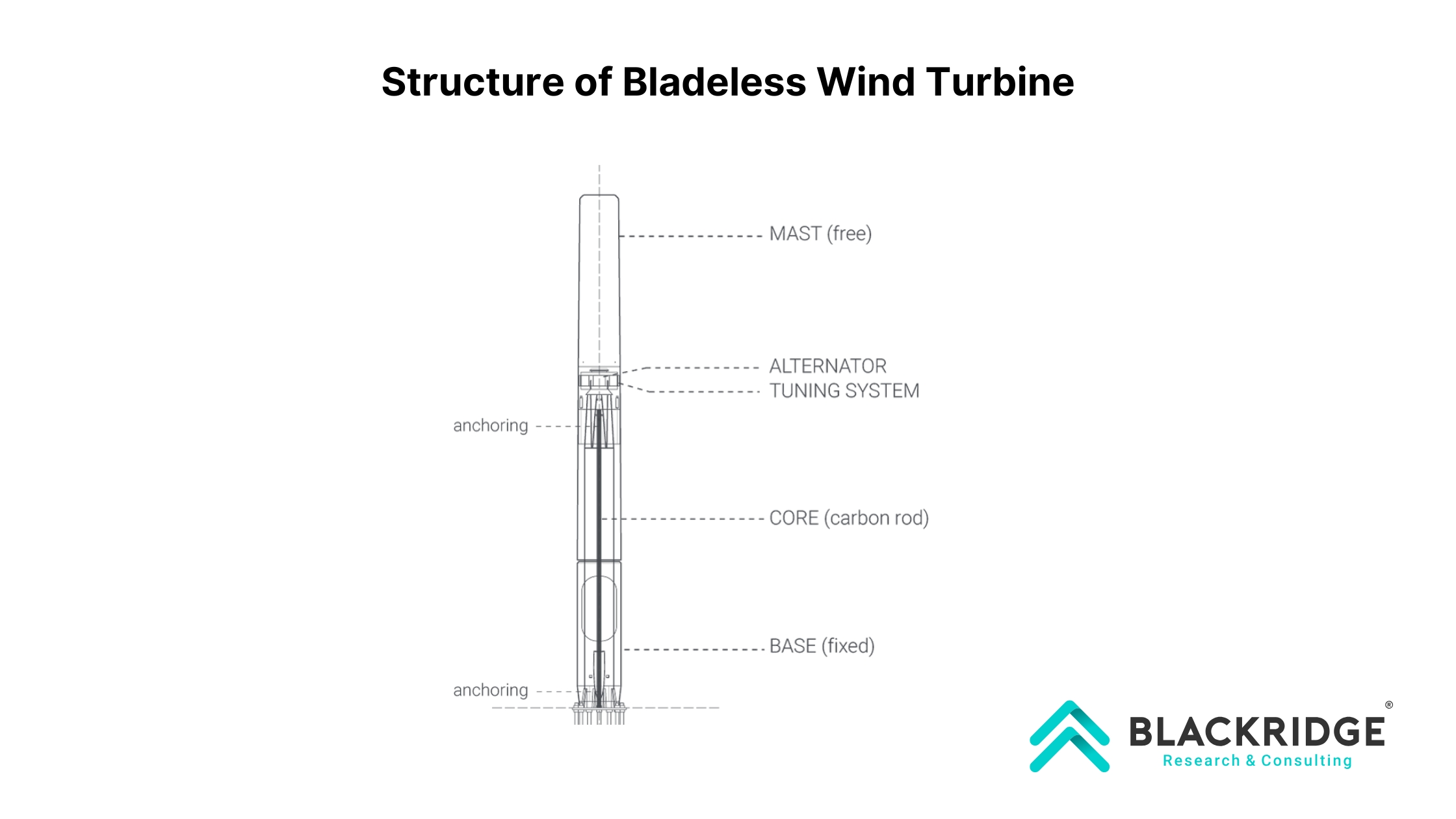
The structure of a bladeless turbine is simple yet effective. It consists of a flexible cylinder anchored to the ground by a sturdy rod, with the top of the rod supporting the cylinder. Made from lightweight and durable materials like carbon or glass fiber, the turbine is designed to oscillate as wind flows around it.
The absence of blades makes these turbines quieter, less expensive to maintain, and safer for wildlife while still capturing wind energy efficiently through their unique design and operation.
Bladeless wind turbines are of different types; each type uses wind's kinetic energy to run a specific mechanism for green energy generation. Some of the most known mechanisms are vortex-induced vibration and charge displacement through wind.
Advantages of Bladeless Wind Turbines
Bladeless Wind Turbines have more advantages compared to traditional wind turbine blades; they are:
- Bladeless vortex devices come without nacelles, support systems, or blades, making them easy to manufacture, install, and operate.
- Without the mechanical elements, the system requires less maintenance and has a prolonged life. They don't even require lubricants in the long run.
- Bladeless wind turbines adapt faster to changes in wind direction, which makes them more suitable for urban and rural areas.
- Bladeless wind turbines are designed with very low swept areas that reduce environmental impact by avoiding bird strikes, noise pollution, and visual impact.
- Bladeless turbines can operate both on and off the grid, and they can also be used in hybrid wind-solar projects.
- Energy efficiency is higher than normal wind turbines and can able to operated under low speed wind conditions.
Looking for Global Wind Power Market Report? Download Free Sample Now!
Disadvantages of Bladeless Wind Turbines
Bladeless wind turbine technology is still in the development stage. Let’s look into some of the disadvantages of it:
- Bladeless wind turbines produce 30% of wind energy, which can be obtained from traditional turbines.
- Their design restricts them to lower heights and limits access to stronger and more consistent winds.
- It is not possible to produce electricity on a large scale like a wind farm.
Difference Between a Bladeless Wind Turbine and Traditional Turbine
| Feature | Bladeless Turbine | Traditional Turbine |
| Design | Bladeless | Bladed (3 blades typically) |
| Gearbox | Gearless | Often requires a gearbox |
| Lubrication | Oil-less | Requires lubrication (gearbox) |
| Braking | No braking needed | Requires braking systems |
| Orientation | Always oriented (by design) | Requires yaw mechanism for wind direction adjustment |
| Fabrication | Easier fabrication (potentially) | More complex fabrication (blades, gearbox) |
| Foundation | Similar foundation requirements | Similar foundation requirements |
| Wind Range | Small wind range (maybe less efficient in low or very high winds) | A wider range of wind speeds for efficient operation |
| Space Required | Less space required (potentially) | Requires more space due to rotor sweep area |
| Lifespan | Potentially greater lifespan (due to fewer moving parts) | Shorter lifespan due to wear and tear on components |
| Current Status | Under Development | Mature technology |
Major Types of Bladeless Wind Turbines
Here are some of the major types of bladeless wind turbines:
EWICON Bladeless Wind Turbine
![]()
EWICON stands for Electrostatic Wind Energy Converter. It utilizes wind to create a flow of charged particles through the air that can be tapped into to produce electricity. In this case, water droplets are used to hold a positive charge, and when the wind blows them, this movement of the droplets produces electricity that can be transferred to the grid.
The current design comprises a steel frame that supports a horizontally oriented set of insulated tubes. Each tube has many electrodes and nozzles that release positively charged water particles into the air on a regular basis.
Like ordinary wind turbines, the device can be deployed on land or at sea, but the design is particularly suited to metropolitan environments. Due to a shortage of space, large wind farms are usually not viable in larger cities, but one or more EWICONs might be fitted into existing buildings simply by modifying their design.
The only disadvantage of the technology is the need for a continuous supply of water.
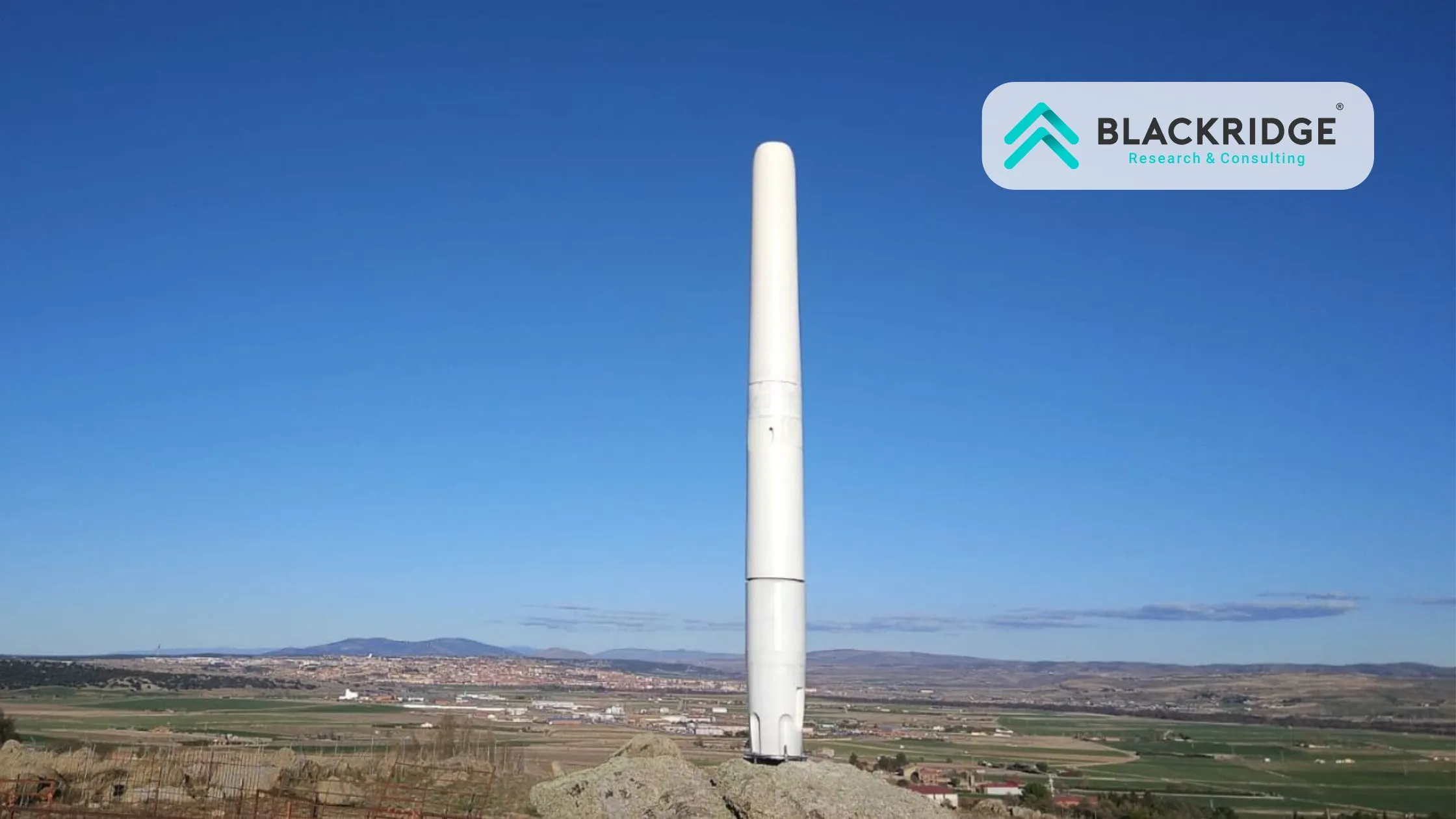
Vortex Bladeless Wind Turbine

Vortex Bladeless is a vortex-induced vibration resonant wind generator. Vortex Shedding, a phenomenon of vorticity, is used to harvest wind energy. Bladeless turbine technology is essentially a vertically fixed cylinder with an elastic rod. A wind range oscillates the cylinder, which generates electricity via an alternator system.
The outer cylinder is made to be mostly rigid, yet it can vibrate while being tethered to the bottom rod. The top of the cylinder is unbound and has the largest oscillation amplitude. The vortex turbine structure is made of polymers reinforced with carbon and glass fiber, which are commonly used in wind turbine blades to harness wind energy.
The mast is supported at the top of the rod, while the bottom is firmly fixed to the ground. It is made of carbon fiber reinforced polymer, which has a high fatigue resistance and low energy leakage when oscillating.
Vortex wind turbines start generating power at a wind speed of 3 m/s and automatically stop working when the wind speed exceeds 30 to 35 m/s. Vortex systems operate on low to medium wind speeds and generate the same amount of energy at a cost 45% lower than that of a conventional turbine. The cost of a vortex wind turbine is around 200 euros.
The material costs of the vortex turbines have been reduced because of their simple shape and light weight of 15 kg. The manufacturing costs of vortex device is estimated to be about 53% of that of a conventional wind turbine. Due to its bladeless architecture, the turbine is noiseless (below 20 Hz). Also, the operating life of the bladeless wind generator is calculated between 32 and 96 years.
Vortex Bladeless Ltd. is the leading company in bladeless wind turbine technology, holding 33.6% of the market share. The company is currently developing three models: Vortex Nano, Vortex Tacoma, and Vortex Atlantis/Grand. Vortex Nano is a 1-meter tall unit with a 3 W output, which is designed to complement solar panels.
Vortex Tacoma, standing 2.75 meters tall with a 100 W output, is suited for residential and farmland applications. Vortex Atlantis/Grand is a prototype measuring 9 to 13 meters with a 1 kW output currently targeted at residential, rural, and factory installations.
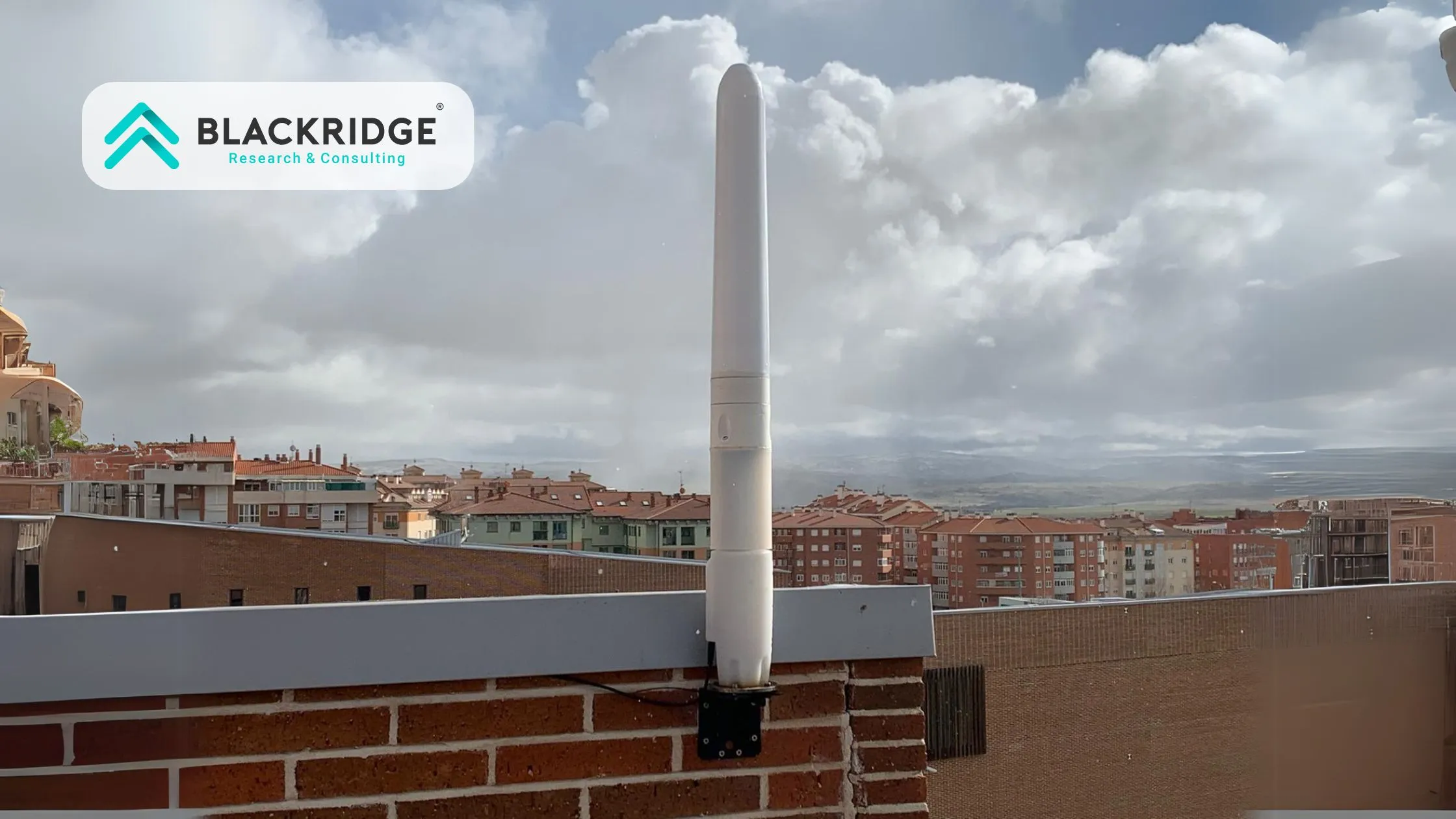
PowerPod

Halcium, a Salt Lake City-based firm, is developing the PowerPod, a small-scale wind turbine that may be used in cities. It is the most powerful and safe wind turbine ever, according to its makers. It's a 1 kW wind turbine that can generate three times the power of a standard turbine. The extra power comes from the pod's innovative blade technology, which increases wind speed by 40%.
It also has no moving parts on the outside, which poses no danger to birds. The PowerPod can be operated on its own, connecting to a power supply in the same way as solar panels do and requiring similar equipment. The PowerPod is designed to integrate easily with solar PV to give a second, varied source of clean energy.
As wind speed increases due to the device's design, it becomes less necessary to attach the PowerPod on tall poles, which are costly to install and take up a lot of room if guy wires are required.
The system can be utilized in both public and private spaces, and it has the potential to become a simple and rapid addition to building systems, allowing them to generate their own electricity rather than relying on the grid.
SWET (Solid State Wind Energy Transformer)
.webp)
The Solid State Wind Energy Transformer functions in a similar fashion as the EWICON but instead of water, SWET uses coronal discharge to create negative air ions, which the wind carries away from the SWET. The SWET harnesses wind-induced currents and voltages to produce electrical power. The technology produces very little electricity and is in the early stages of development.
Bladeless Wind Turbine Market 2025
Bladeless wind turbines are still in their infancy and consequently less efficient in converting captured wind power into electrical energy, which limits their widespread use. However, with future design and development of sophisticated technologies and superior materials, demand for bladeless wind turbines is expected to increase in the coming years.
Blackridge Research’s Global Bladeless Wind Turbine Market Report predicts growth of the Bladeless wind turbine market, USD 162.8 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 9.1%. The study examines the drivers, restraints, and regional trends influencing global bladeless wind turbine market demand and growth.
On a global level, the bladeless wind turbine market is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in technology, environmental concerns, and rising interest from diverse sectors. The integration of smart materials and IoT enhances the efficiency and appeal of bladeless turbines with low maintenance benefits.
Looking for Global Bladeless Wind Turbine Market Outlook? Download Free Sample Now!
The governments support this through subsidies and favorable policies. Also, the telecom sector dominates applications due to the turbines' suitability for remote and off-grid locations. Regionally, North America holds 39.5% of the bladeless wind energy market, valued at USD 25.4 billion.
A further advancement in technology is that Aeromine Technologies secured USD 9 million in Series A funding to scale its motionless wind energy units in 2024. This system generates 50% more energy than rooftop solar at the same cost. The technology uses aerodynamics to capture airflow and requires 10% of the space of solar panels.
A 10-unit system can produce up to 150,000 kWh annually, depending on wind speed and roof height. Aeromine plans to launch commercially in Europe and North America by 2025, targeting industrial, commercial, and government sectors.
Explore Bladeless Wind Turbine Market Outlook
Discover Blackridge's Global Bladeless Wind Turbine Market Outlook to 2028 to gain valuable insights into this innovative renewable energy solution. Understand market trends, opportunities, and the potential of bladeless wind turbines to revolutionize the energy sector.
What’s Inside?
- In-depth analysis of the bladeless wind turbine market
- Key drivers, challenges, and growth opportunities
- Industry trends shaping the renewable energy landscape
- Comprehensive answers to your FAQs
Download Your FREE Sample Report Now!


![Top 10 Wind Turbine Models in the World [2025]](https://images.blackridgeresearch.com/zA7C1E09-z4Uj64Eb0zfkw/9b62c6ed-bf95-451c-7b9e-5fa68b44ac00/public)



Leave a Comment
We love hearing from our readers and value your feedback. If you have any questions or comments about our content, feel free to leave a comment below.
We read every comment and do our best to respond to them all.