Table of Contents
Geological hydrogen is a naturally formed hydrogen gas beneath the earth's surface. It is formed through geological processes such as serpentinization. The hydrogen gas found beneath the rocks serves as natural geological hydrogen storage.
So why is geological hydrogen in demand? It naturally occurs underground in large quantities and its purity makes it different from the other sources and forms of hydrogen. Also, it emits low greenhouse gas emissions, which is the need of the hour!
Furthermore, geological hydrogen provides energy security and supports the transition towards a greener future. Its flexibility in transportation & storage makes it one of the potential future source of hydrogen!
But how is geological hydrogen produced - “Earth’s Hydrogen Factory.”
Geological hydrogen is produced naturally underneath earth surface, however countries like Russia have explored new ways of producing geological hydrogen underneath earth surface by injecting oxygen, a catalyst, and water vapor underground. This method is yet to be perfomed by the Russian government and is in early stages.
Serpentinization
It is known as one of the most common geological processes that take place underground to produce geological hydrogen. This process is best observed in tectonic plate boundaries and mid-ocean ridges.
In this process, iron-rich minerals olivine and pyroxene react with water under high pressure and temperature conditions. This causes olivine minerals to convert to a group of hydrated magnesium silicate minerals called serpentine minerals.
During this conversion process, hydrogen gas is released. The hydrogen gas produced is stored underneath the rock formations which can be used as a geological hydrogen storage and can be extracted later.
Radiolysis
Radiolysis is when radioactive elements interact with water molecules underground to produce hydrogen gas and oxygen. Often, radiolysis is observed naturally occurring within certain rock formations due to certain radioactive elements present in the rock.
Radioactive elements such as uranium or thorium are usually present within rocks in small quantities that emit radiation, which reacts with the water molecules, breaking the water bonds to produce hydrogen and oxygen gas.
Disadvantages of Radiolysis
Radioactive element disposal can lead to increased environmental risks.
Rock Crushing
The fault lines in between the rocks can be responsible for producing hydrogen gas as H2 molecules at the mineral surfaces of the rocks.
Degassing
Hydrogen can be produced form the center of earth's crust during the formation of earth's core through a process called degassing.
Where can I find Geological Hydrogen?
Geological hydrogen is found underneath the earth’s surface and formed between rocks through geological processes.
What is the largest source of hydrogen on earth?
Natural gas is considered the largest source of hydrogen on earth; however, geologists predict that natural hydrogen energy underneath the earth's surface can be one of the largest sources of hydrogen due to its naturally occurring process.
Where is natural hydrogen found in the US?
The geography of the United States is such that large amounts of clean natural hydrogen can be accumulated and extracted from both the coasts and the Midwest.
What is the difference between gold and white hydrogen?
White hydrogen or geological hydrogen is formed between rocks below the earth's surface through geological processes on the converse, gold hydrogen is formed through microbial activity in depleted oil wells.
Where is the most common place to find hydrogen?
Hydrogen is scarce as gas and abundantly available as molecules or atoms in living things such as water, plants, humans and animals.
Where is hydrogen naturally found on earth?
Hydrogen is found naturally underneath the earth's surface along with other elements and compounds such as oxygen, hydrocarbon, and fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum.
How do you extract hydrogen from the ground?
The geological hydrogen can be extracted through processes like drilling into underground reservoirs or fracking by injecting a mixture of water, sand, and chemicals under high pressure to release gas from rocks or through geological processes such as serpentinization.
Geological Hydrogen Storage
Geological hydrogen storage is a naturally formed underground hydrogen storage with irregular capacities and sizes used for storing the hydrogen formed beneath the rocks through geological processes.
The geological hydrogen storage is formed naturally underground and provides several benefits:
- Naturally formed with large capacities that reduce the additional cost of infrastructure storage facilities.
- Geological hydrogen storage ensures the safety of potential hydrogen leaks and explosions.
There are several types of geological storage, such as salt caverns, depleted gas fields, and aquifers.
Salt Caverns: These are the underground cavities formed by dissolving salt deposits which are used for hydrogen storage. It is one of the most popular hydrogen storage methods.
Depleted Gas Fields: Often, the natural gas fields are reused as hydrogen storage facilities once the natural gas is extracted.
Saline Aquifers: Aquifers are formed through different types of rocks such as sandstone, conglomerates, gravel and limestones.
How much does Natural Hydrogen cost?
Natural or gold hydrogen in naturally occurring gas form can be extracted at a cost of less than USD 1/kg. This costing is less compared to the production of hydrogen from natural gas at USD 3.70/kg and from coal at USD 4.20/kg.
The cost of producing hydrogen from renewable energy sources is highly expensive. The costing ranges from USD 4.22/kg up to $16.80/kg.
Potential Impact of Geological Hydrogen
Geological hydrogen also referred to as white, gold, or natural hydrogen, is considered as a “game changer” for the hydrogen industry. Several countries, such as the US, Canada, Australia, Colombia, France, Spain, and South Korea, are exploring geological hydrogen production.
Initially, it was discovered in Mali in 1987; two decades later, geological hydrogen is considered gold and is currently used to power the Malian village of Bourakébougou.
Several new technologies, such as hydrogen-sensing gas probes, use spectrometers to detect & measure dissolved hydrogen at depths of up to 1,500 meters. Probes to detect dissolved hydrogen at deeper levels of 3,000 meters are currently under development.
Recently, the world’s largest geological hydrogen deposit was found in France’s eastern Lorraine region. According to Geoffrey Ellis, a research geologist at the Energy Resources Program of the USGS (US Geological Survey), there is likely to be about 5 trillion metric tons of geologic hydrogen beneath the earth's surface.
Russia recently announced its new way of producing geological hydrogen. In this method, Russia will inject oxygen, a catalyst, and water vapor into the ground (natural gas cuts) so that underground natural gas ignites with the injection to create an explosion. This explosion leaves behind by-product of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. During the explosion, a layer is formed that allows only hydrogen to pass through into the collection containers, leaving behind the carbon monoxide in the ground.
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced that USD 20 million will be used to support about 16 geological hydrogen projects across the country.
On February 26th, 2024, the USGS and Colorado School of Mines established a joint industry program to promote geologic hydrogen. This program aims to identify potential geological hydrogen resources in the United States and develop extraction strategies across the country.
Around eight industry partner companies are involved in this program, which are: BP, Chevron, Geopower, Petrobas, Fortescue, Koloma, Hydroma USA and HyTerra.
Geological Hydrogen Companies
Below are a few companies that extract geological hydrogen from rocks:
HyTerra
It was the first company to list on the ASX (Australian Securities Exchange Ltd) with a focus on white hydrogen (geological hydrogen). Nemaha in Kansas, USA, is one of their prestigious white hydrogen projects. This project covers approximately 52,000 acres and has wells with more than 10 hydrogen and helium occurrences within the region.
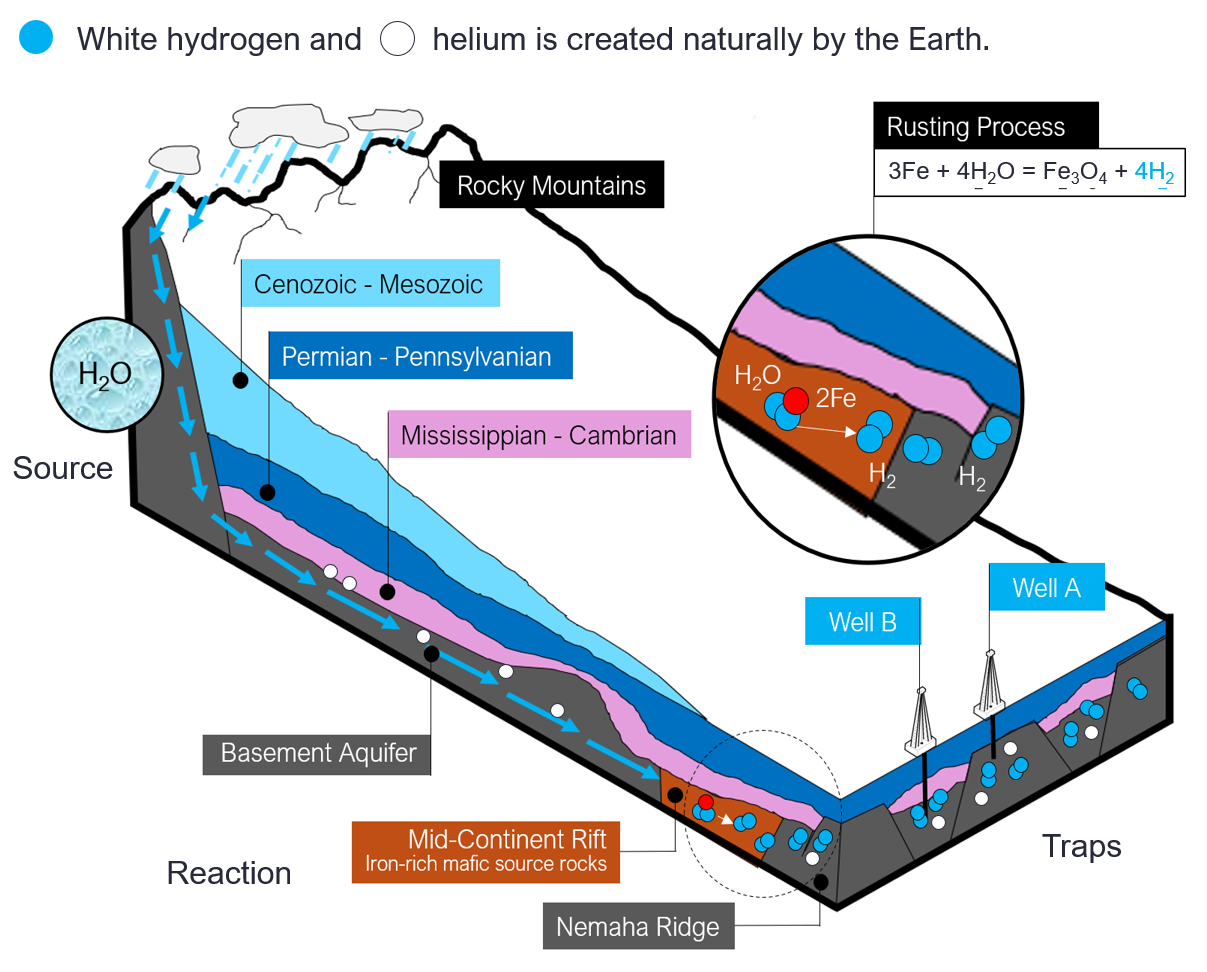
Formation of geological hydrogen at Nemaha project, USA
At the Nemaha project, rainwater seeps underground where it reacts with iron-rich rocks at high temperatures, producing hydrogen. This process is referred to as "rusting." The hydrogen produced is brought to the surface using conventional oil and gas techniques.
Hydroma
Hydroma is among the companies that run several exploration campaigns for geological hydrogen. From 2017 to 2019, about 24 wells were drilled within 10 km of Bourakebougou.
Back in 2012, Hydroma performed a Bourakebougou pilot project in Mali. This pilot project included electricity production from natural hydrogen (geological hydrogen) for the first time in the world.

Electricity production from geological hydrogen at Bourakebougou
For more than 7 years, the village of Bourakebougou has been using electricity from white hydrogen (clean hydrogen) without carbon dioxide emissions. The electricity here is produced from white hydrogen from a nearby well and is supplied to an internal combustion engine. The quality of this natural hydrogen is said to be 98% pure.
With more such projects, Hydroma intends to improve energy in the African Continent across several rural and urban areas.
Get your hands on latest hydrogen fuel cell market report. Claim Your Free Leads Now!
Koloma
Koloma is a US-based geological hydrogen company that primarily focuses on hydrogen production methods in a clean, cost-effective manner. Koloma is known for its data-driven approach in geological hydrogen industry exploration activities, thus playing a key role in US decarbonization efforts.
Studies performed by Koloma show that geological hydrogen originates from iron-rich rocks with organic rock matter. Geological hydrogen can be produced with low carbon intensity, with no external energy & water inputs, and with minimal surface disruption.
Recently, on 15th October 2024, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries agreed to fund the geological H2 exploration by Koloma.
Cemvita
Cemvita takes CO2 and waste streams to produce proteins, plastics, and fuel feedstock. It uses microbes to absorb and convert CO2 into molecules needed to build a renewable future.
It specializes in CO2 based manufacturing that converts CO2 and methane into industrial chemicals, biomining, subsurface biomanufacturing and is now into geological hydrogen.
It launched a gold hydrogen program for subsurface biomanufacturing of hydrogen. It was launched as a pilot of the microbial gold hydrogen process during the 2nd week of the American Hydrogen Forum.
Get your hands on latest hydrogen fuel cell market report. Claim Your Free Leads Now!
Geological Hydrogen vs. Other Hydrogen Sources
|
| Geological Hydrogen | Grey Hydrogen | Blue Hydrogen | Green Hydrogen |
| Occurrence | Natural | Natural Gas | Natural gas | Renewable energy |
| Process | Naturally occurs deep within the Earth's crust | H2 separated from CH4 | H2 separated from CH4 | H2 separated from H2O |
| Carbon emissions | No emissions | High carbon emission | Moderate carbon emissions | No emissions |
| Carbon Capture | Not Required | No carbon capture | Carbon emissions are captured | Not Required |
| Cost | Cheapest Hydrogen to produce | Not costly | Costly | Very expensive |
| Uses | Power generation, transportation fuel, industrial processes | Industrial processes, fertilizer production, refining | Industrial processes, transportation fuel, power generation | Transportation fuel, power generation, industrial processes |
Geological Hydrogen Uses & Benefits
Geological hydrogen, or natural or white hydrogen, have several uses and potential benefits of this hydrogen:
- It can be used in transportation through the potential alternative of hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEV).
- Use in electricity generation as an alternative to fossil fuels.
- To produce low-carbon feedstock for ammonia production and steel making.
- For generic heating purposes.
Geological hydrogen offers several benefits, making it a potential renewable clean energy source. Its benefits include:
- Abundant supply under the earth's surface.
- Geological hydrogen storage allows no additional infrastructure storage.
Conclusion
Geological hydrogen is formed under the earth's surface through geological processes. It differs from the other forms of hydrogen and is inexpensive in production compared to other renewable sources such as green hydrogen. Apart from this, geological hydrogen is produced with zero carbon emissions compared to blue hydrogen or grey hydrogen.
Countries like New Zealand, France, Australia and the USA are investing into natural hydrogen exploration through research and pilot projects. Thus, geological hydrogen (pure hydrogen) will prove to be a golden source of energy in the future.
FAQs
Is there natural hydrogen on Earth?
Yes, the naturally occurring hydrogen underneath the rocks through geological processess is called geological hydrogen.
What is the geological storage of hydrogen?
Geological hydrogen storage is a vast underground storage space that is void of oxygen, and hydrogen can be stored in large volumes.
What are the 4 types of hydrogen?
Natural or white hydrogen (geological hydrogen), blue hydrogen, grey hydrogen and green hydrogen are a few popularly known types of hydrogen.
What rocks produce hydrogen?
Hydrogen is often produced from iron-rich rock such as peridotites, which undergoes chemical reactions when they interact with water to produce hydrogen as a byproduct.
Looking for a detailed hydrogen fuel cell market overview?
The use of FCEVs has increased drastically, which is supported by government regulations. Major car manufacturers such as Toyota, Hyundai and Honda have included FCV cars in their portfolio. Countries like South Korea, the USA and China are predominant in the hydrogen fuel cell industry.
The use of hydrogen fuel cells in transportation, power generation, and backup has increased drastically over a few years.
Want more insights about the hydrogen fuel cell industry?
Get your hands on Blackridge's Global hydrogen fuel cell market report that covers:
- Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Drivers & Restraints
- Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Analysis
- Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Size & Demand Forecast
- Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Industry Analysis
- Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Segmentation and Forecast
- Regional Market Analysis
- Key Company Profiles
- Competitive Landscape and a
- Executive Summary
Why Blackridge's Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Report?
- Rigorous analysis across multiple regions
- Understanding the driving forces of the industry to improve your company strategy
- Exclusive access to market size data complied with future demand forecast
- Understand the emerging market trends through statistical representations
- Stay updated about industry players
To learn more about the report and our other current offers, contact us!







Leave a Comment
We love hearing from our readers and value your feedback. If you have any questions or comments about our content, feel free to leave a comment below.
We read every comment and do our best to respond to them all.