Table of Contents
The Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM) was implemented in January 2016 under the supervision of Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari. The purpose of this initiative was to encourage new investments in road infrastructure projects in India. The Hybrid Annuity Model has become highly relevant, particularly after the Budget 2022-23, which emphasized enhancing India's infrastructure considerably. Around 51% of the 1900 km of road projects have been granted under HAM by the National Highway Authority of India during the first half of the fiscal year 22.
Let's delve further and gain a comprehensive understanding of the Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM) / HAM project
What is Hybrid Annuity Model?
The Hybrid Annuity Model combines Engineering, Procurement, Construction (EPC) and Build, Operate, Transfer (BOT). 40% of this combination is the EPC model, while the remaining 60% is the BOT-Annuity model.
Photo: Delhi Mumbai Expressway
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) pays forty percent of the overall project expenditures per the Hybrid Annuity Model. The release of this payment is divided into ten equal installments, each dependent upon the successful accomplishment of specific project objectives. The road developer is responsible for arranging the remaining sixty percent of the fund. A portion of the project cost, around 20 to 25 percent, is financed by the developer. The remaining portion of the funds is obtained through debt collection.
Explore Global Construction Projects and TendersClaim you free leads!
What is the EPC Model?
The EPC model, which stands for "Engineering, Procurement, and Construction," is a method of constructing infrastructure in which the government pays private firms to construct roadways. After the completion of the road, the private participants are no longer responsible for anything. They are not involved in the ownership of roads, the collection of tolls, or the maintenance of roads. These things are under the authority of the government.
Read: What is an EPC contract?
What is the BOT- Annuity Model?
The BOT (Build, Operate, Transfer) infrastructure construction model involves private firms' participation over an extended period. They are responsible for constructing, operating, and maintaining the roads for a predetermined amount of time, for example, ten to fifteen years. Following that, the ownership of roads is returned to the government. The private parties are responsible for securing funding for the project following the BOT model. To construct and maintain the roads, the private players receive a certain amount of money as an annuity. BOT-Annuity is the name given to this particular annuity charge.
Read: All You Need to Know About BOT (Build Operate Transfer) Project
How does HAM Work?
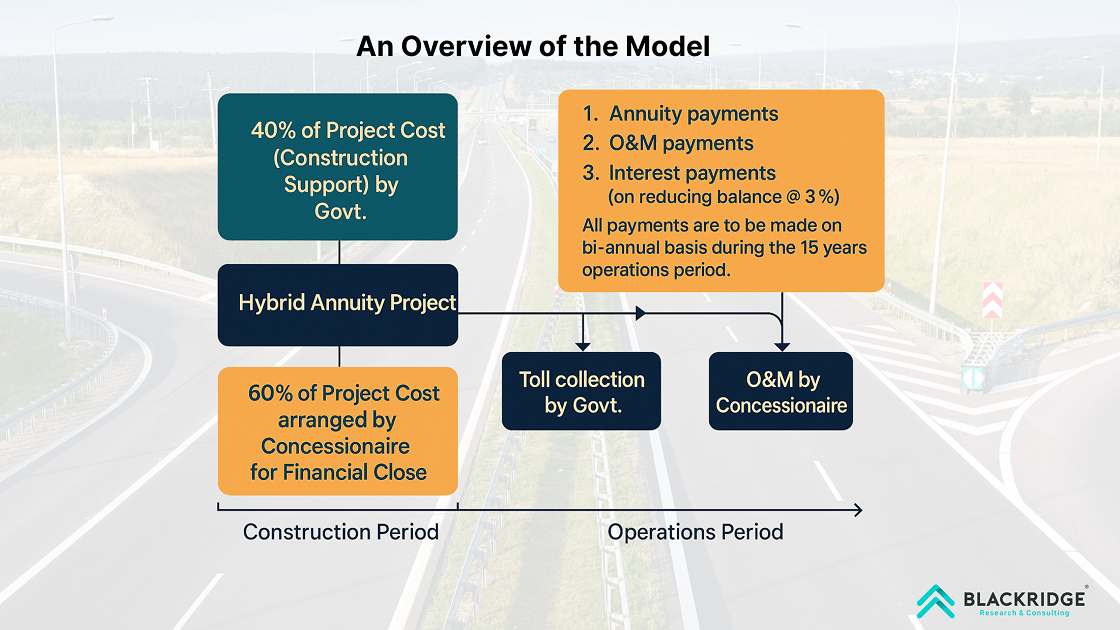
The Hybrid-Annuity Model (HAM) involves the government offering a predetermined payment to the private developer (concessionaire) as an annuity over the concession period, which usually spans 15-20 years. The annuity payment sufficiently covers the expenses incurred by the developer and ensures a satisfactory return on investment. The developer takes over responsibility for the project's design, construction, funding, and operation throughout the concession period. Upon the expiration of the concession period, the project's ownership is handed to the government.
Key Features of the HAM Model
Here are some important features of the HAM model,
The concessionaire for the project is chosen through a bidding procedure that is both open and competitive.
Life Cycle Cost serves as the single bid parameter.
The concessionaire is responsible for ensuring that the project is maintained until the conclusion of the concession period.
The concession period encompasses both the duration of construction and a fixed period of 15 years for operations.
The government is responsible for the collection of tolls.
Explore Global Construction
Projects and Tenders Claim you free leads!
The Importance of the Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM) in India
The Hybrid Annuity Model has the potential to provide support in enhancing the country's infrastructure investment. It may result in commutes that are both more efficient and more beneficial. The model is very useful in India because of the following reasons,
When compared to the BOT model, the HAM model has been successful. Private players were unwilling to invest under the BOT model because they were required to raise the total quantity of money through either equity or loans.
It is essential to have the HAM model because it allows for the risk of any project to be split between a private player and the government.
Developers are protected from the "traffic risk" risk by a payment structure based on annuities. Because of this strategy, the government can construct roads and generate higher social returns, which is a significant advantage.
Launching and completing road projects can result in improved road conditions, more comfortable journeys, and less congestion.
Key HAM Projects
Here is a list of a few projects under the Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM) in India, along with their completion and start dates:
PROJECT | START YEAR | COMPLETION YEAR |
Delhi-Meerut Expressway | 2018 | 2021 |
Purvanchal Expressway | 2018 | 2021 |
Nagpur Mumbai Samruddhi Expressway | 2022 | 2024 |
Lucknow Ayodhya Expressway | 2023 | 2025 |
2022 | 2025 |
Conclusion
In summary, the hybrid annuity model (HAM) demonstrates the concept of a public-private partnership (PPP) by distributing the obligations and risks of a project between the two parties involved. Under this contract, both public and private entities have specific responsibilities to complete the project. Therefore, the degree of participation of contractual parties in the hybrid annuity model (HAM) is significantly greater as compared to the engineering, procurement, construction (EPC) and the build, operate, transfer model (BOT).
FAQ's
What is the HAM model?
HAM refers to Hybrid Annuity Model. It is a mix of EPC and BOT models: ham project meaning.
What is the difference between HAM model and BOT model?
In BOT, the concessionaire must put all the money into the business. Most projects get 70% of their money from debt and 30% from stock. That means the developer has to put up 30% of the equity cash. In HAM, the government only pays for 40% of the project's cost. The developer has to pay the other 60%.
Is the Hybrid Annuity Model a type of PPP infrastructure construction model?
The Hybrid Annuity concept is a modified version of the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) concept.
Is the change of ownership allowed under the Hybrid Annuity Model?
Ownership transfer under the Hybrid Annuity Model is permissible after six months from the commencement of commercial operations.
What is the interest rate for Hybrid Annuity Model highway projects?
According to the Hybrid Annuity Model, the interest rate applied to the highway projects will be equivalent to the one-year MCLR average of the five most prominent commercial banks plus another 1.25 percent.
Connect with decision-makers of the global Construction plant projects for business opportunities.
Subscribe to upcoming and ongoing construction projects and tenders global database to access reliable and high-quality insights on upcoming, in-progress, and completed construction/EPC projects globally.
Our user-friendly platform provides essential details, timely updates, key stakeholder contact information, and business opportunities tailored for engineering companies, industry professionals, investors, and government agencies.
Start a free demo to take your business to the next level


![List of Top 5 Largest Construction Companies in Portugal [2025]](https://images.blackridgeresearch.com/zA7C1E09-z4Uj64Eb0zfkw/2b549578-fd97-4e1a-6ee2-9094c80f6400/public)




Leave a Comment
We love hearing from our readers and value your feedback. If you have any questions or comments about our content, feel free to leave a comment below.
We read every comment and do our best to respond to them all.