
Understanding Global CO2 Emission and Its Multifaceted Risks
Table of Contents
Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions have become a global concern due to the adverse consequences they bring. Whether it is global warming or uncertain climate patterns, carbon dioxide emission has garnered attention from both the political class and scientific communities alike.
To make informed decisions and effective plans to reduce these emissions, a carbon footprint analysis is required. This blog aims to provide a clear overview for all the stakeholders concerned with global CO2 emissions.
Understanding the Sources of Carbon dioxide
Human activities are the main reason there's so much CO2 in the air since the Industrial Revolution. The biggest source is burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas for energy, making up about 60% of global CO2 emissions. Coal is especially bad, releasing almost twice as much CO2 as natural gas for the same amount of energy. This highlights the need to shift to cleaner energy sources.
Find Global CCUS Projects and TendersGet Started Now!
Apart from energy production, industries also play a big role in CO2 emissions. For example, making cement produces about one ton of CO2 for every ton of cement, making it crucial to find ways to reduce emissions in this sector. Changes in how we use land, like cutting down forests or harming the soil, also release stored carbon into the air, making the whole CO2 emission situation more complex.
Understanding Global CO2 Emissions by Sector
Evaluating the relative emission impact of different activities or sectors requires tools like emission intensity. This metric expresses the average amount of CO2 emitted per unit of activity, such as energy produced or economic output. Analyzing emission intensity across different sectors helps identify areas with the highest reduction potential and inform targeted policy interventions. For example, the electricity sector presents a crucial area for emission reduction efforts, particularly in regions heavily reliant on coal-fired power plants.
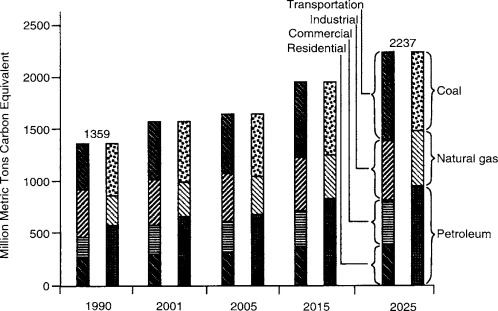
Energy Production
- Fossil Fuels: Coal, especially in Southeast Asia and China, releases a lot of CO2 when burned for electricity. Natural gas is cleaner but still emits CO2, and leaks during extraction and transport add to emissions.
- Renewables: Solar and wind produce little to no CO2, but we need more of them to offset fossil fuel emissions.
Manufacturing
- Iron and Steel: Making iron from ore using coal emits a lot of CO2. Processes like steel rolling add to emissions.
- Cement: Making cement releases a large amount of CO2 directly. Operating kilns also contributes to emissions.
- Chemicals: Producing ammonia, plastics, and industrial chemicals emits varying amounts of CO2.
Transportation
- Road vehicles: Cars and trucks burning gasoline and diesel are major contributors, despite some improvements in fuel efficiency.
- Aviation: Jet fuel combustion and contrail formation in the sky lead to significant emissions.
- Shipping: Heavy fuel oil in ships is a highly polluting source, and increasing seaborne trade adds to emissions.
Also Read: All You Need to Know About Carbon Capture Utilisation and Storage
Measuring Emission of Carbon dioxide
Quantifying world CO2 emissions accurately is essential for tracking progress and evaluating mitigation strategies. Scientists utilize various units, including kilotons (kt) for large quantities and grams of CO2 equivalent per unit of activity for comparing annual CO2 emissions worldwide and studying its impacts across different sectors.
However, capturing the complete picture demands consideration beyond traditional fossil fuel-based emissions. Accounting for land-use changes and incorporating the contributions of other greenhouse gases like methane and nitrous oxide are crucial for comprehensive measurements.
Understanding the Impacts of CO2 Emissions
CO2, along with other greenhouse gases, plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's energy balance. These gases trap heat radiating from the planet's surface, leading to a gradual warming effect. The increased atmospheric CO2 concentration observed since the Industrial Revolution has directly contributed to global warming, characterized by rising average temperatures. This has led to altered weather patterns and several other cascading environmental consequences.
Greenhouse effect
CO2, along with other gases, acts like a warm blanket around Earth. It keeps the heat from escaping, causing our planet to gradually get warmer. The temperature has gone up by more than 1 degree Celsius since the olden days because of this.
Rising sea level
Oceans are getting warmer, and thus expanding their coastlines. Melting ice from polar regions are adding to the misery. This is bad news for places near the coast. It can damage buildings, force people to move, and make the coast erode. Scientists say sea levels could go up a lot by the end of the century if we keep releasing lots of CO2.
Weather going extreme
The Earth's air patterns are getting messed up due to global warming. This makes extreme weather happen more often, like super hot days, droughts, floods, and big storms. These extreme events can mess up farming, make it hard to get enough food, and damage homes and roads. The world has seen more of these extreme weather events recently because of CO2 emissions.
Find Global CCUS Projects and TendersGet Started Now!
Ocean acidification
A Quiet Danger: Oceans take in a lot of the CO2 we make. This changes the water, making it more acidic. The acid can hurt sea creatures that make shells and skeletons, like corals and shellfish. This messes up the whole ocean ecosystem and the food chain.
Trouble for agriculture
Higher temperatures, strange rain patterns, and more extreme weather make farming tricky. Crops might not grow well, and there might not be enough water. Bugs that eat crops might become a big problem. This can make it hard for people in some places to have enough food to eat, especially where they already struggle with not having enough food.
Cascading effects
The problems caused by CO2 emissions are all connected. For example, when sea levels rise, it can make flooding worse, especially during storms. The oceans getting warmer and more acidic can hurt sea life even more. To fix these problems, we need to look at all the connections and come up with smart plans that cover everything.
Also Read: Global Top 10 Carbon Capture Companies [2024]
The Future Outlook
Studying the total global CO2 emissions by industry, it is evident that the power (particularly oil and gas) and industrial process sectors are the largest contributors when it comes to carbon emission footprint. Fast forward to 2050, and the crystal ball, aka the International Energy Agency (IEA), suggests their share in the annual global CO2 emissions will drop to around 50% from the current 60%.
So, how do these sectors pump out all that CO2? Well, it's the classic move of burning fossil fuels in is boilers and furnaces, belching it out from those colossal exhaust stacks. We call these stacks "large stationary sources" because they're unlike emission sources like automobiles or household appliances.
Interestingly, these massive stationary sources can be a jackpot if the CO2 is diverted for some other use instead of just emitting it to the environment. That's where CCUS (Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage) technology can be a game changer.
By deploying CCUS methods for carbon capture, industries can get rid of their huge amounts of emissions. CCUS projects around the world can be captured and converted into high-purity CO2 for storage. This stored CO2 can then be deployed for beneficial uses.
However, not all the power and industrial emissions take place from a single point. Refineries, for instance, have stacks on stacks, presenting a real challenge when trying to fit an exhaust-gas gathering system into an already crowded party scene. It's like trying to find space for your friend's pet elephant at a house party – technically challenging and likely to jack up the costs.
CCUS as a potential solution for reducing carbon emissions
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) is a multifaceted process that involves the extraction of carbon dioxide (CO2) primarily from major source points. These points are largely present in power generation or industrial activities that rely heavily on fossil fuels or biomass. The carbon dioxide is then utilized for other beneficial purposes.
If the on-site utilization of the CCUS method proves impractical, the captured CO2 can be compressed, stored, and subsequently transported through pipelines, ships, railways, or trucks. Alternatively, the extracted CO2 can also be utilized in sequestration processes within deep geological formations. These formations can be from depleted oil and gas reservoirs or saline aquifers.
Conclusion
Understanding CO2 emissions and their impact on climate change is no longer a scientific curiosity but a vital component of informed decision-making and responsible action. This paper has presented a concise overview of the sources, measurements, and consequences of CO2 emissions, highlighting the need for collaborative global efforts to mitigate their impact and ensure a sustainable future for our planet.
Also Read: Unveiling the Potential of Carbon Sequestration in Heavy Industries
Discover CCUS projects with ease
Are you looking for a platform that gives you reliable, high-quality, and timely project insights for CCUS projects around the world?
Discover the Global Project Tracking (GPT) platform by Blackridge Research, designed to provide you with the most recent CCUS Projects and Tenders around the world better and faster across various stages of development:
- Upcoming projects
- Tender Notices
- Contract award announcements
- Projects in progress or under construction
- Successfully completed projects.
The user-friendly interface helps you obtain early-stage awareness of projects and find the right business opportunity quickly.
Each project will have all the essential details, such as scope, capacity, CapEx, status, project description, companies involved, funding information, location, periodic updates, important event dates like construction start date, commissioning dates, and key contact information of project owners and stakeholders.
The database is a vital resource for a wide range of entities, including energy companies, industrial manufacturers, technology providers, investment firms, government agencies, regulatory bodies, research institutions, environmental consulting firms, utilities, and grid operators, renewable energy developers, and carbon offset market participants.
Book a Free demo to learn more about the global CCUS projects database and how we can help you achieve your goals






Leave a Comment
We love hearing from our readers and value your feedback. If you have any questions or comments about our content, feel free to leave a comment below.
We read every comment and do our best to respond to them all.